BLOOD SUGAR CONTROL AND MANAGEMENT
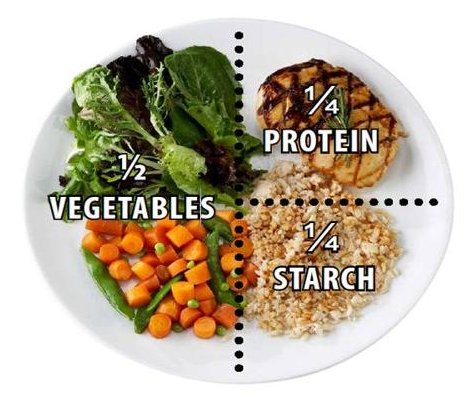
PORTION CONTROL
Portion control involves regulating the amount of food you consume in one sitting to manage caloric intake and maintain a balanced diet.
some tips for effective portion control:
- Use Smaller Plates: Smaller plates can make portions appear larger, helping you feel more satisfied with less food.
- measure your food: Use measuring cups, spoons, or a kitchen scale to serve accurate portions.
- Read Food Labels: Check serving sizes on nutrition labels to understand how much you’re consuming.
- Pre-portion Snacks: Instead of eating directly from the bag, portion out snacks into small containers or bags.
- Eat Slowly: Take your time to eat, which can help you recognize when you’re full.
- Avoid Eating from Large Packages: Serve food onto a plate instead of eating straight from the package.
- Be Mindful of Liquid Calories: Beverages can add up quickly, so measure drinks like juice, soda, and alcohol.
- Plan Meals and Snacks: Preparing meals and snacks in advance can help you control portions better.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Pay attention to what you eat and how much, focusing on your hunger and fullness cues.
- Eat More Frequently: Smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent overeating at main meals.
.

Importance of consistent meal sizes
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Consistent meal sizes help maintain steady blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can lead to fatigue, irritability, and cravings.
- Metabolism Balance: Regular, balanced meal sizes support a stable metabolism, aiding in efficient energy use and reducing the risk of weight gain.
- Digestive Health: Predictable meal sizes can improve digestive efficiency, reducing the risk of bloating, discomfort, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Weight Management: Consistency in portion sizes can help control caloric intake, supporting weight management and preventing overeating.
- Nutrient Intake: Balanced meal sizes ensure a consistent intake of essential nutrients, contributing to overall health and preventing deficiencies.
- Hunger and Satiety Signals: Regular meal sizes help your body maintain a rhythm, allowing hunger and fullness cues to function correctly, which can prevent overeating or undereating.
- Energy Levels: Consistent meal sizes provide a steady supply of energy throughout the day, enhancing physical and mental performance.
- Hormonal Balance: Regular meal patterns can help regulate hormones related to hunger and satiety, such as ghrelin and leptin, promoting better appetite control.
- Improved Mood: Stable blood sugar levels and adequate nutrient intake contribute to better mood regulation and reduced risk of mood swings.
- Long-term Health: Consistent portion sizes and regular eating patterns are associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.